Lecture #1: Microscopy
and the Ubiquity of Microorganisms
I. ________________________ is the study of ____________________________ _______________________________________________. Special techniques are required to isolate, grow and or visualize these agents and microorganisms.
II. Ubiquity and Importance of Microorganisms
A. Where are microorganisms?
1. _________________________
2. food
3. water
4. _________________
5. clothing
6. _____________________
7. air
8. ________________________
9. acid
10. __________________________
11. feces
B. Where aren’t they?
1. _____________________________________________________
2. In the interior of a healthy human body, excluding the digestive
tract (e.g. _________________, cerebral spinal fluid,
________________, bone marrow, urine while it’s
in the bladder).
C. WITHOUT MICROBES:
1. _____________________________________________________
___________________________________ and dead plants and
animals would not even decompose.
2. Without photosynthetic microorganisms, _____________________
_______________________________________________________.
3. ______________________________________________________
______________________________________________________.
D. Despite the ubiquity of microorganisms, they ____________________ __________________________________. Sterile media stays sterile until inoculted and then if inoculated with a single microorganism, the culture is a _________________________________. (*Pure cultures are very uncommon in nature.) When working with sterile media and pure cultures, it is important to use sterile technique.
III. Microscopy
A. Types of microscopes:
1. _________________________________________________
Forms a ____________________________________________
________________________________________.
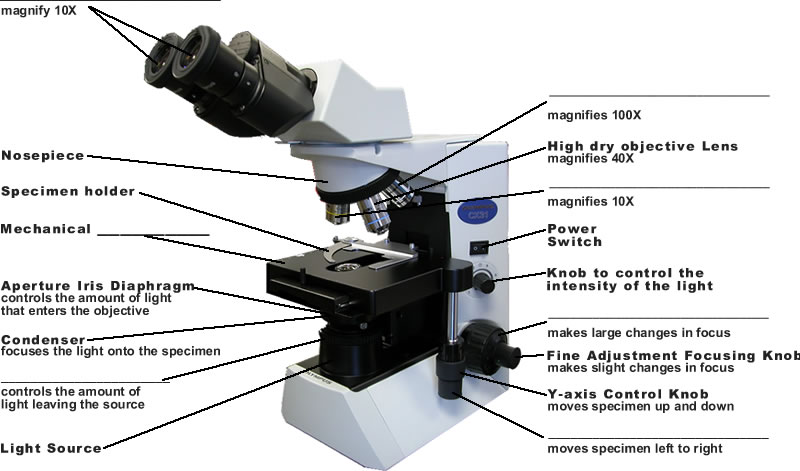

B. A light microscope is a collection of mirrors and
lenses. Microscope lenses act like a ___________________________________________:
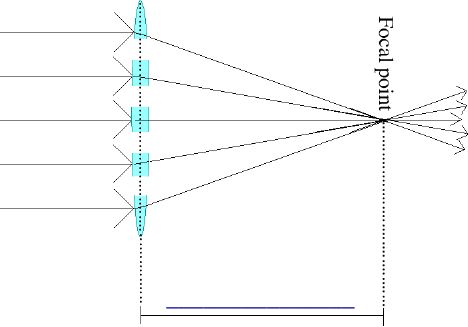
D. Magnification and Resolution
1. Magnification
a. The process of __________________________________
as an optical image.
b. The shorter the __________________________ (above)
the greater the ____________________________.
c. The total magnification of a microscope is the ____________
of the magnifying power of the _________________
and the ____________________ lenses.
What is the total magnification of our light microscopes if the
40X objective lens is being used?
______________________________
2. Resolution
a. The _____________________________________
objects that are _________________________________.
The better the resolving power, the closer the objects can be
and still be seen as _______________________.
b. Resolution is ___________________ when ______________
wavelengths of light are used.
c. Lenses with _______________________________________
have shorter _____________________________________
and better resolution.
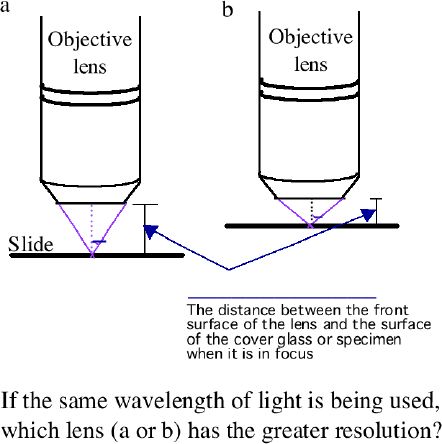
d. Immersion oil
1.) Oil has the _________________________________ _________________.
2.) Rays that would not enter the objective in air, due to reflection
and refraction, can do so in oil. This effectively ___________________________________________.
3. Parfocal
- In a microscope that is parfocal, the image should _______________
___________________ when the objective lens is changed.
4. Determining the _______________ of objects
a. Size can be estimated by first calculating the _____________
of the field of view at 100X total magnification. This can be
done by viewing a ruler etched on a glass slide.
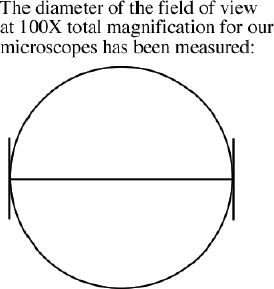
b. Now, by estimating ________________________________ ________________
by a microorganism, size can be estimated.
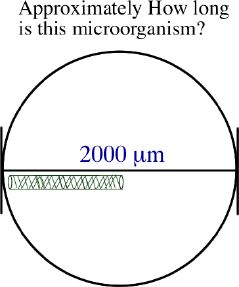
c. There is an ____________________ relationship between
the ______________________________________ and the ___________________________________.
The greater the magnification, the closer the object appears and
the smaller the size of the field.

How much of the field of view would the microorganism above take
up if the total magnification was 400X?
|






