Lecture #2
Simple Stains: Direct and Negative
In the last lab we viewed samples (____________________________)
under the microscope. This is a fast way to view ____________________________
that is ___________________________________________.
We were able to make true assessments of ______________________________________________________.
However, these wet mounts are _____________________________
and can be a potential _____________________________________________.
I. ____________________ samples (smear
preparations)
A. Fixation
1. _______________ fixation:
simultaneously ___________________ __________________________________.
This is the ____________ __________________
fixation method.
2. _______________________ fixation:
has the same results as the heat fixation. Examples of chemical fixatives
are alcohol and formaldehyde.
B. Disadvantages of a fixed sample
1. Can’t observe specimen ___________________________.
2. Causes a slight _________________________________________.
C. Advantages of a fixed sample
1. ___________________________
- can be used for long-term study.
2. The preparations _________________________________
(below) to enhance contrast and reveal specialized cell structures (e.g.
flagella, endospores, capsules, cell walls etc..)
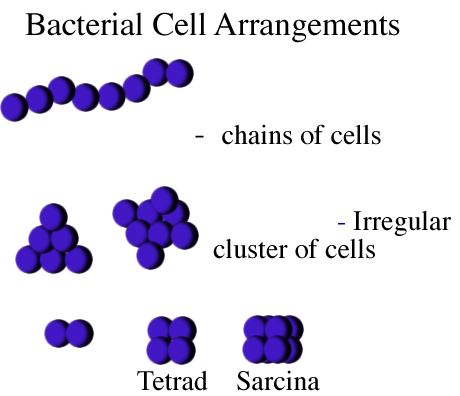
Bacterial Cell Shapes
We will deal mainly with the two most common shapes:
_____________________: 
____________________: 
II. The composition of a stain
A. Solvent
B. Solute = contains ____________________________________,
which are highly conjugated and give the dye its _________________.
1. ______________________________________________
dyes
a. Contain ________________________
charged groups, which bind to __________________________________________.
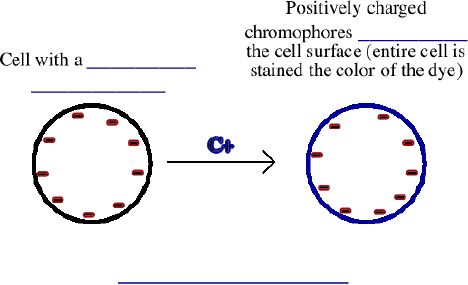
b.Direct dyes are the _______________________________
and examples include methylene blue, basic fuchsin, crystal violet,
safranin and malachite green.
http://homepages.wmich.edu/~rossbach/bios312/LabProcedures/Simplecocci.jpg
c. Applied to bacterial smears that have been _______________
_______________.
2. __________________________________dyes
a. Possess ___________________________________________ such as carboxyls (-COO-) and hydroxyls (-OH-).
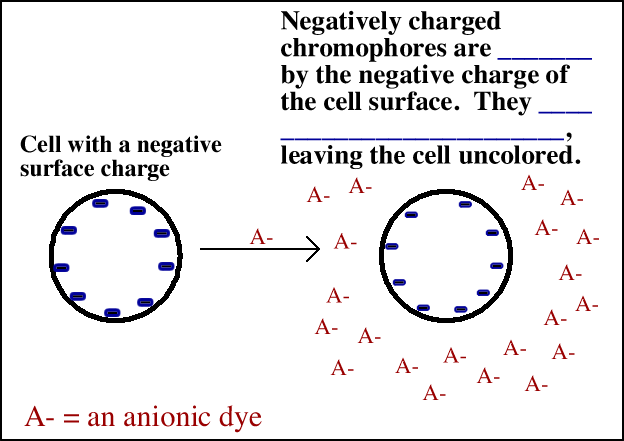
b. Can be used to determine morphology and cellular arrangement
in bacteria that are ____________________
______________________________________________.
III. Stain categories
A. __________________________________
(today)
1. Uses a _________________________
(acidic or basic) and all organisms take on the ______________________________
.
2. Is a ____________________________ method to determine cell size,
shape and arrangement.
B. _____________________________________
(Labs 3 and
4)
1. Divides bacteria into ________________________________based
on staining properties.
2. Is ___________________________ but the color of staining gives
information _______________ ________________________ in addition
to size, shape and arrangement.
IV. Processes used in the identification of bacterial unknowns:
A. _________________________________ (staining)
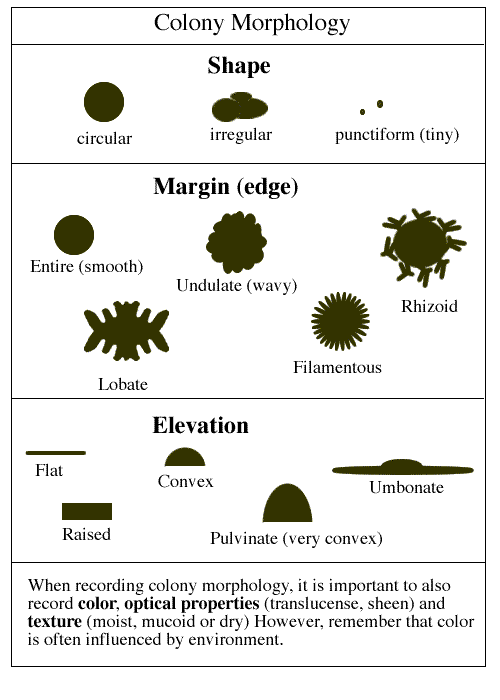
B. _______________________ (e.g. type of colony and
time it takes to grow) and _______________________ _________________________
(e.g. carbohydrate fermentation and production of virulence factors.)
- Results can be coupled with a __________________________________.
(Dichotomous keys for the first unknown identification can be found
under additional information on the lab home page. It's not too soon
to print those off!)
|






