Lecture #11 and 12: Bacteriophages
I. Bacteriophages (or Phages)
A. A bacteriophage is a ______________
that uses a _________________
as its host cell
B. It is an ___________________________________________________.
C. Phages have either an RNA or DNA genome which:
1. Directs _________________________.
2. Directs synthesis of a ___________________________________
that protects and transmits the genome between cells.
D. Viruses are ______________________________________.
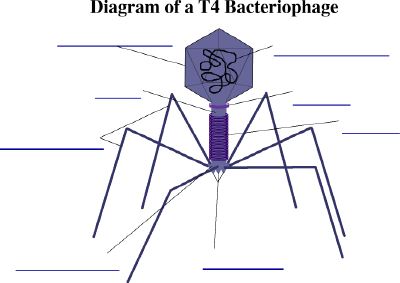
II. Types of Bacteriophages
A. ____________________—phages
that multiply rapidly in host cells and then destroy them through
lysis (the _____________________________).
Bacteriophage T4 is a virulent phage.
B. _______________________—phages
that can follow either the lytic or lysogenic pathway (lambda bacteriophage)
In the lysogenic pathway, phages produce a repressor protein that
prevents the replication of phage DNA. Instead this DNA is _______________________
into the host cell’s chromosome and the phage is then called
a ________________________. The
host cell will then replicate and produce daughter cells that contain
the prophage within their DNA. These cells are called _________________________
bacteria.
III. Lytic Phage Replication Cycle (based on bacteriophage T4 of E.
coli)
A. Step 1: ____________________
1. Adsorption proteins on the phage tail fibers attach to ___________
___________________________ on the surface of the bacterial
cell.
2. As more tail fibers make contact with the bacterial cell, the
______________________________________
on the cell surface.
B. Step 2: ________________________
1. Conformational changes occur in the phage tail and the _______________________________________.
2. The phage genome is _____________________
out of the phage head, through the core and _________________________________
___________________________.
C. Step 3: ________________________
The phage ________________________
transcription and translation of the bacteria’s mRNA. The host
RNA polymerase starts synthesizing phage mRNA encoding for protein
factors and enzymes required to ____________________________________________,
degrade host DNA and manufacture viral nucleic acids.
1. _________________________
of the phage genome are made.
2. Many copies of the _____________________________________
______________________________________ are also produced.
D. Step 4: _________________________
Capsid head and the tail proteins are ___________________________
into mature phage particles and the DNA is _____________________
within the phage head. The newly assembled phages are called _______________________________________.
E. Step 5: _________________________
Daughter phages lyse the host cell and are released to
infect other bacteria.

IV. How to isolate viruses.
A. First, the host (bacteria, mammalian cells, etc.) has to be ______________________
with the virus. The virus is then able to replicate and is _________________________.
B. Next, the host cell must be __________________. This allows the
viruses to ________________________________________________ (liquid
in which the cells were grown).
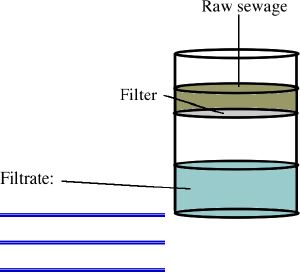
C. The supernatant is then ____________________. The filter allows
the viruses to pass through with the fluid, but does not allow pieces
of the lysed cells to pass.
D. The end product is a fluid that should __________________________
__________________________. Last lab we spotted this fluid onto 3
quadrants of a TSA plate inoculated with E. coli. Today we
should see a lawn of E. coli with some small ____________________________
where phages have infected and lysed the bacteria. These clear zones
are called ________________________. Remember that theoretically,
__________ ____________________________________________________________.
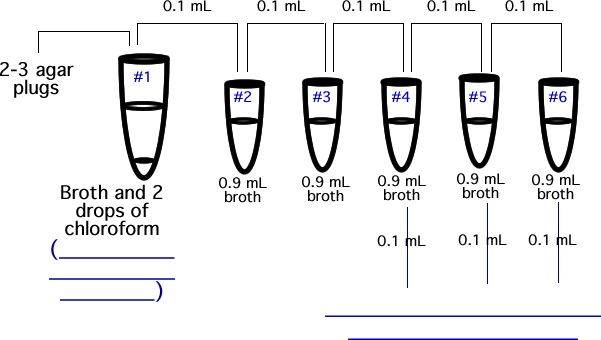
V. Determining bacteriophage titer
Viruses are too small to be seen using a light microscope so we look
at plaques to determine their titer.
A . Titration of bacteriophage
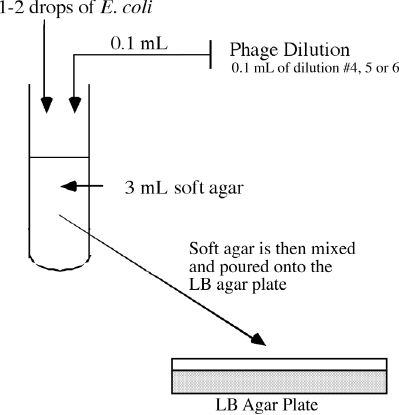
B. ______________________________________
traps the E. coli and the diluted virus between the two layers
of agar leading to _________________ ________________________________________________________.
Notes:
*Make sure everything is ready before you go to the water baths so
the soft agar ________________________________
prematurely.
*Next time we will count the plaques and determine the virus titer.
|




