LECTURE 24: ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY II
SOIL MICROBIOLOGY
Soil is made up of 5 major components: _____________________________
________________________________________ (from decaying biomass)
________________________________________________ (plants, animals
and _______________________________).
The soil is a very favorable habitat for a wide range of microorganisms, including
___________________________________, algae, _____________
and protozoa. Their presence makes the soil a suitable site for ____________
______________________ and many ______________________________.
Soil microorganisms are important in:
1. Biogeochemical cycles
They ____________________________________ and ______________
________________________________ such as ____________________
__________________________ and sulfur. Ecosystem would collapse
without microorganisms in the soil ______________________________ ______________________.
2. Biopesticides
Proteins produced by some bacteria have been used to ______________
______________________________. A toxin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis
is so useful that the gene that encodes for the toxin was isolated from the
bacteria and ________________________________ ________________________________________.
These genetically transformed ____________________ and ________________________
plants are now able to produce the _____________________________,
and protect themselves against damage by ______________________ such
as moths and worms. Bacillus thuringiensis has also been used to control
________________________ and _______________________.
3. Sources of antibiotics. – You are already familiar with use of
soil microorganisms as sources of several antibiotics.
The accurate enumeration of microorganisms in the soil is difficult because
culture methods reveal only those few microorganisms which can grow in the
______________________________________________________. Direct
microscopic examination of soil is also difficult and would not reveal virus
particles or differentiate _________________________________________.
Although many groups of microorganisms occur in the soil we will attempt to
isolate only 3 different groups:
1. _________________________________
a) Belong to the group _______________________________ which
are abundant in most soils
b) Although they are bacteria, they _____________________________
in overall morphology by forming branched filaments or ______________________.
At the tip of the hyphae they produce _______________________,
a type of ______________________ _____________________________
unrelated to endospores.
c) Produce a compound called ____________________, which gives
the soil the characteristic ________________________________.
d) Are sources of several ______________________________ such
as ______________________________ produced by Streptomyces
griseus. The presence of these antibiotics in a soil will affect
and sometimes determine the _________________________________
and abundance in that soil.
e) ____________________________________ is used for enrichment
of members of the Streptomyces genus.
2. _________________________________________
Although the soil is home to a vast number of bacterial species, less
than 5% of the soil bacteria have been ___________________________ and
__________________________. Generally there are more __________
__________________ bacteria in soil. However, some Gram-positive bacteria
reside in the soil such as the members of the genera _______________
and ____________________. Both of these genera ____________________________________,
which enable them to survive prolonged periods of ___________________________________
________________ such as ___________________ and ______________________________________.
Common Gram-negative bacteria found in the soil include _______________________________,
Cellulomonas, ________________________ and
Xanthomonas. If soil is contaminated with _________________________
it may contain ________________ __________________________________
such as ________________ _______________ and _________________________________
- but these bacteria are normally eliminated rapidly from the ecosystem by
competition. ________________ will be used to select for these
bacteria.
__________________________________
The plant cover in the soil is an important factor in determining the types
and numbers of microorganisms in that soil. ____________________________
is the zone of soil that adheres to plant roots and is enriched with nutrients.
Plant root exudates and senescent parts of plant excrete organic molecules
including ____________________________________________ and ____________________
and can be an important source of nutrients for soil microorganisms. At the
rhizosphere there are _________________________ than in the
surrounding soil. The rhizosphere also enhances ____________________________________________.

Scanning electron micrograph demonstrating the colonization of wheat roots
by strains of Azospirillium
_____________________
Fungi are found mainly in the top 10 cm of the soil and are most abundant
in __________________________________. Fungi are __________________,
and _______________________________ to degrade decayed plants
and animals for their nutrient supply. Many soil fungi metabolize ________________________,
including complex _____________________ such as _____________________________________.
Soil fungi occur as _____________________________________ organisms
or in mycorrhizal association with plant roots. Some soil fungi, especially
those found in association with plant roots, are _______________________
if not impossible to ___________________________ and isolate
in the lab.
In order to isolate fungi, we will use _______________________________,
which:
is __________________________: Streptomycin and Rose Bengal
Dye inhibit the growth of bacteria and other non-mold soil organisms.
contains a _________________________________________ which favors
mold growth.
Nitrogen fixing bacteria
The ______________________ is one of the most important biogeochemical cycles with which microorganisms are involved.
Nitrogen is an essential building block for all amino acids and many other macromolecules. Unfortunately, most nitrogen exists as N2 gas which is not usable by most organisms. Thus, N2 must be converted to more usable forms of nitrogen such as ________ and ________. The conversion of N2 (g) to NH3 is called ____________________ ___________________.
______________________________
b. Nitrogen fixation by prokaryotes is responsible for transforming _______________ of naturally occurring usable nitrogen forms.
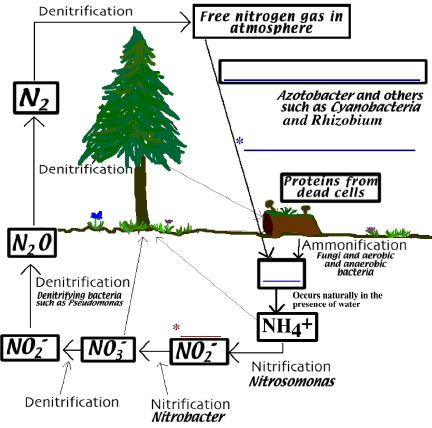
c. Common nitrogen fixing bacteria found in soils include the _________________________
nitrogen fixing bacteria and the ___________________________________
fixing bacteria. The free-living nitrogen fixing bacteria include ________________________
_______________________ and cyanobacteria.
______________________________
Azotobacter is an important free-living heterotrophic ___________
_________________ bacterium, capable of converting atmosphere _____________________.
Free-living nitrogen fixing organisms can be isolated using a __________________________________.
In this medium ____________ organisms that _______________
____________________________ grow. The medium contains
___________________________________ and molybdenum ions which
___________________________________. In today’s lab we
are going to isolate Azotobacter from a soil sample.
Rhizobium
The symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria in soils include the ________________________
which form a symbiotic relationship with _________________________________,
in what is commonly referred to as ___________________________________________.
The rhizobia complex includes Rhizobium, Sinorhizobium, Azorhizobium and
Bradyrhizobium which are common in soil and are able to fix N2
___________________________________________ of legumes. Nitrogen-fixing
root nodule bacteria such as Bradyrhizobium present inside the nodule
provide valuable ___________________________________ to the
host plant, which promotes plant growth. The host plant provides ________________
____________________ to the bacteria.

Root nodules formed on the root system of a soybean plant in symbiotic relationship
with Bradyrhizobium
|