|
IECM 13.1 User Manual > Modules Included with the IECM > Pulverized Coal (PC) Plant > GET RESULTS > NOx Control > 1. In-Furnace Controls > In-Furnace Controls Diagram |
|
The In-Furnace Controls Diagram result screen shows the major flows into and out of the in-furnace controls NOx control technology:
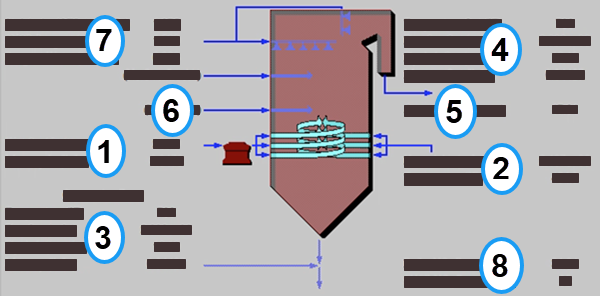
PC: GET RESULTS: NOx Controls: 1. In-Furnace Controls: In-Furnace Controls Diagram
Each result is described briefly below in flow order:
•Area 1: Fuel Entering Boiler:
•Wet Coal In: Fuel flow rate into the boiler on a wet basis. Waste products removed prior to the burners are not considered here.
•Mercury In: This is the mass flow rate of total mercury entering the boiler. The mass reflects the molecular weight of elemental mercury.
•Area 2: Air Entering Boiler:
•Heated Air: Volumetric flow rate of the air at the burners, based on the air temperature at the burners and atmospheric pressure.
•Temperature: Heated air temperature measured at the burners. This is generally determined by the combustion air temperature exiting the air preheater.
•Area 3: Flue Gas Exiting Convective Zone: This the area of the furnace between the combustion zone and the SNCR (if present). Changes in the flue gas after combustion due to in-furnace combustion NOx controls are reflected here.
•Temperature: Temperature of the flue gas exiting the convective zone.
•Flue Gas: Volumetric flow rate of the flue gas exiting the convective zone, based on the temperature exiting the convective zone and atmospheric pressure.
•Fly Ash: Total solids mass flow rate in the flue gas exiting the convective zone. This includes ash, unburned carbon and unburned sulfur.
•Mercury: Total mass of mercury in the flue gas exiting the convective zone. The value is a sum of all the forms of mercury (elemental, oxidized, and particulate).
•Area 4: Flue Gas Exiting the Economizer:
•Temperature Out: Temperature of the flue gas at the exit of the economizer.
•Flue Gas Out: Volumetric flow rate of the flue gas at the exit of the economizer, based on the temperature at the exit of the economizer and atmospheric pressure.
•Fly Ash Out: Total solids mass flow rate in the flue gas at the exit of the economizer. This includes ash, unburned carbon and unburned sulfur.
•Mercury Out: Total mass of mercury in the flue gas exiting the economizer. The value is a sum of all the forms of mercury (elemental, oxidized, and particulate).
•Area 5: Ammonia Slip: (Only shown if the SNCR or LNB & SNCR configuration is chosen.)
•Ammonia Slip: This is the ammonia slip exiting the boiler as a result of unreacted reagent added by the SNCR.
•Area 6: Gas Reburn: (Only shown if the Gas Reburn configuration is chosen.)
•Reburn Gas: This is the flow rate of natural gas into the boiler.
•Area 7: SNCR: (Only shown if the SNCR or LNB & SNCR configuration is chosen.) The SNCR is located in the upper portion of the boiler. Several parameters are reported as a summary.
•Stoic.: This is the actual reagent stoichiometry used in the SNCR. Note that urea has double the moles of nitrogen relative to that of ammonia.
•SNCR Reagent: This is the mass flow rate of reagent (urea or ammonia) injected by the SNCR into the boiler. Note that water used to dilute the urea is included in this flow rate.
•Reagent Water: This is the water used to dilute the reagent.
•Area 8: NOx Removal Performance:
•Boiler NOx Removal: (Not shown if the SNCR configuration is chosen.) This is the composite removal efficiency of the boiler NOx technologies associated with low NOx burners, overfire air, and reburn. It does not include the removal efficiency of an SNCR system.
•SNCR NOx Removal: (Only shown if the SNCR or LNB & SNCR configuration is chosen.) This is the removal efficiency of the SNCR system alone. It does not take into consideration any other NOx reduction prior to the SNCR.
Copyright © 2022-2026 University of Wyoming. All rights reserved. Visit us at https://www.iecm-online.com/