Lecture #10: TransformationI. Bacteria can undergo change to
their DNA in two ways
A. _____________________________
*Remember from lecture 8 = a permanent, heritable change in the genetic
material. There is a change in the chemistry of a gene. This change
is perpetuated ____________________________________ __________________________.
B. Bacterial _____________________________
1. The process in which a new recombinant chromosome is formed
by _______________________________________________ from two
organisms. The genotype of this new chromosome is different than
that of either of the parents. A change in ______________________
usually accompanies this change in genotype.
2. There are three genetic exchange mechanisms that bacteria use.
a. _______________________________: a mechanism where
“naked” DNA is taken up by a bacterium.
b. _______________________________: a mechanism in which
a bacteriophage carries DNA from a donor bacterium to a recipient
bacterium.
c. Conjugation: a mechanism in which DNA is passed via _____________________________________________.
II. Transformation allows bacteria to make a protein (or proteins)
that give them _______________________________ that may be beneficial
for their survival. This also allows scientists the ability to ______________________________
a bacterium to perform certain tasks.
A. In _________________________________, bacteria can be transformed
with genes that enable them to ___________________________________.
B. In medicine, bacteria can be transformed with a gene that enables
them to make __________________________________.
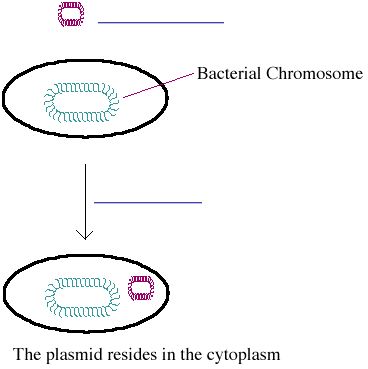
III. DNA that bacteria may uptake can be linear or circular
A. Linear DNA can _____________________ into the bacterium's double-stranded DNA.
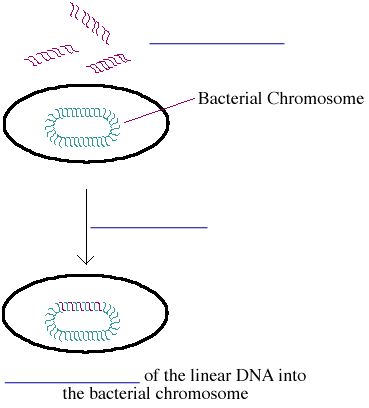
B. Circular DNA (plasmids) will not integrate into host DNA, but instead____________________________________________,
where they will be transcribed and translated to form protein products.
IV. In today’s experiment, we will transform bacteria with a constructed
plasmid called___________________.The pGLO plasmid has three
important genes:
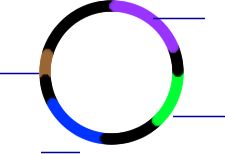
A. The Gene encoding for GFP
1. GFP is the __________________________________________.
2. This gene originates from the ____________________________ ___________________________,
Aequorea victoria.
B. The bla gene
1. encodes for beta-lactamase, an _________________________ that
will allow transformed bacteria to be _______________________ to
antibiotics that have a beta-lactam ring (e.g. ampicillin).
2. Because of this new antibiotic resistance gene in the transformed
bacteria, we can _____________ for their growth using a media that
contains ______________________.
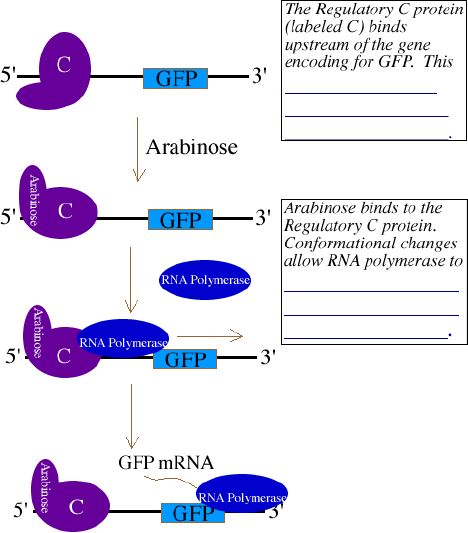
C. The araC gene
1. encodes for a _______________________________________ called
Regulatory C protein. In nature, the Regulatory C protein stops
the production of the enzymes needed to digest the simple sugar
______________________, if this sugar is _____________________ in
the environment.
2. Regulatory C protein binds upstream of the arabinose digestive
genes and ______________________________________________. When arabinose
is present, the Regulatory C Protein changes conformations and _______________________________________
_________________ the needed genes.
3. In pGLO, the arabinose digestive genes _____________________
_______________________ by the gene encoding for the Green Fluorescent
protein. Thus, __________________________________ ________________________________________________________.
V. Methods
A. CaCl2 - often used to render bacterial membranes more _______________
________________________.
B. Heat shock - _______________________ DNA uptake
C. Glucose - allows for quick cell recovery
|



