Lecture #15: Enzyme-Mediated Biochemical Activities of Bacteria: Physiological Testing I
I. Unknown identification
A. __________________________________
1. __________________________________ from the environment of interest (this will vary depending on the researcher’s interest. It may come from soil, spoiled food, or it may be a patient sample: urine, feces, sputum, throat or skin swab, blood)
2. Obtain the organism in a ________________________________ using selective and differential media.
B. ___________________________________________
1. Perform a _______________________________
2. Determine the organism’s unique biochemical properties:
a. Nutrient utilization
b. Resistance to _________________________________________(i.e.
salts, antibiotics, etc.)
c. _________________________
production (catalase, coagulase, hemolysins, oxidase, etc.)
d. _________________________
e. Fermentation
_______________________________
II. Bacterial groups
A. _______________________________________
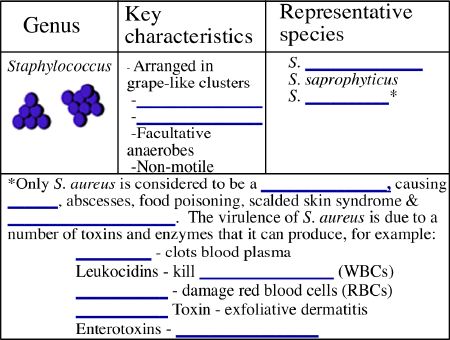
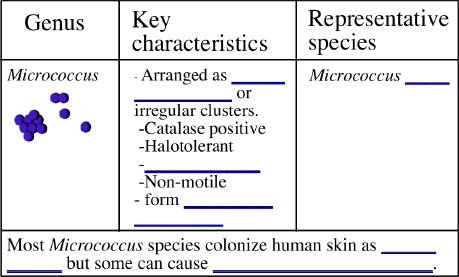
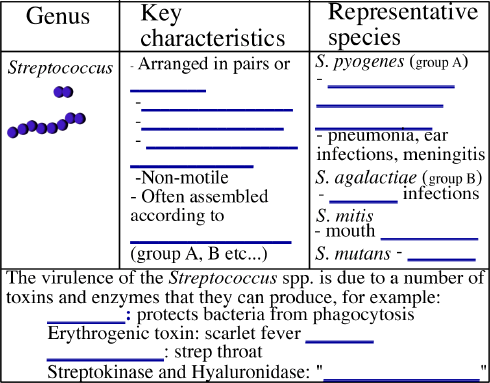
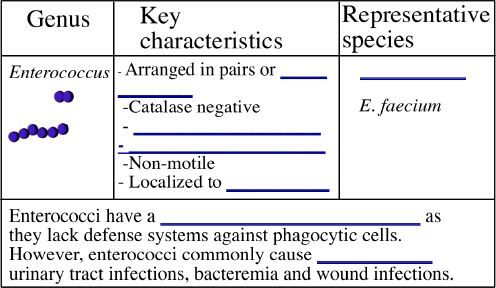
**Practice: A scientist is trying to identify an unknown bacterial isolate.
She finds that the unknown is a Gram-positive cocci. She sees both chains
and irregular clusters on the Gram-stain. What test would she do next? _______________________________________
B. Gram-negative bacilli
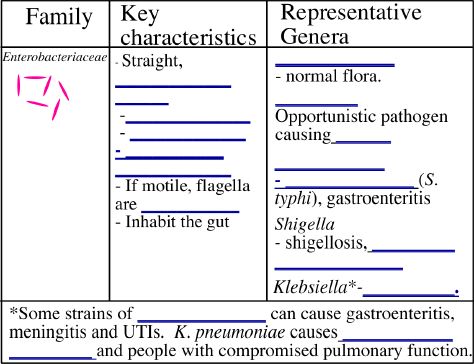
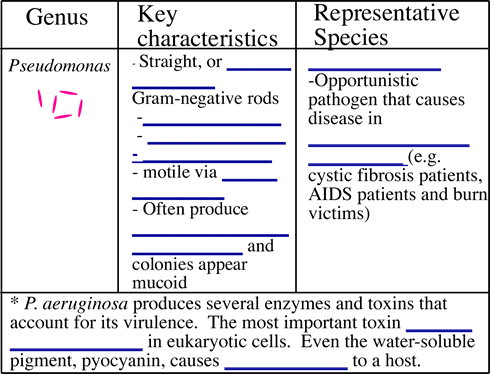
**Practice: A student has a bacterial unkown that is a Gram-negative rod.
What test would the student do first to determine if his unknown is a Pseudomonas
spp. ______________________________________
III. Media and Biochemical Tests
A. Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
This is a very rich medium that allows for the growth of most organisms, but
is also able to differentiate organisms based on their ____________________________________________.
1. Gamma (__)—______________________________
(no clearing zones)
2. Alpha (__)—partial hemolysis
(___________________________________surround
the colonies)
3. Beta (__)—complete hemolysis
(______________________________
surround the colonies)
Which bacterial species discussed above are beta-hemolytic? ______________________________
and _________________________
Which species are alpha-hemolytic? ___________________________
and ________________________
See the summary of
biochemical tests (BAP)
B. Mannitol Salt Agar (7.5 % NaCl)
-Selects for organisms that can live in the ___________________________________________________
and differentiates organisms that can ______________________________________________________.
The agar will turn __________________________
if the organism is able to ferment mannitol due to the acidic byproducts
of the fermentation.
See the summary of biochemical
tests (MSA)
C. Glucose Fermentation Broth tubes
These tubes contain the simple ______________________________________
in addition to a _________ _____________________,
and a __________________________________.
A positive reaction will turn the broth _____________________________________.
The Durham tube will measure ____________________________________
by the bacteria (gas produced by an enzyme called ____________________________________________________).
See the summary of biochemical
tests (Glucose broth tubes)
D. SIM Tube (Sulfur, Indole, Motility)
__________________________________
production will turn the agar ___________________.
Adding Kovac’s reagent, and ______________________________________________________
determine indole production. Indole is produced from the breakdown of the
amino acid ________________________.
Motility is determined by observing the organsim’s ability to move through
the _______________________ ____________________________.
See the summary of biochemical
tests (SIM)
***You will be expected to know the basis for each test ***
and the KEY physiological characteristics of each bacterial genera & species
that we will use in all of the following laboratory periods!!! The culmination
of the next few labs will enable you to take a bacterial unknown and identify
its genus and species based on these tests!!!
Just FYI—you may want to make a flashcard for each test telling you the
positive reaction/color & negative reaction/color & any biochemical
reaction that is taking place for that specific test. In addition, flashcards
relating information for the bacterial organisms will also come in handy!
Another useful tool for this section of lab is your picture atlas—it
has everything in there you could ever want to know about any of the
biochemical tests, media, and positive/negative reactions. The on-line summary
of biochemical tests also serves as a good resource and one that is more specific
to the experiments performed in this class.
|