THE VIRTUAL EDGE: Lab 6 Cultivation of Bacteria II |
|
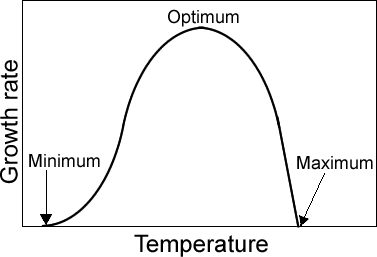
Temperature:The rates of chemical reactions in a cell are determined by the activities of its enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, substances that increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being permanently altered or consumed. The temperature range over which a microorganism grows reflects the temperatures at which its enzymes function. Within this range, three cardinal temperatures can be identified: minimum, optimum and maximum growth temperatures. |
|
| Lab 6 / Pure Cultures: Streak Plate Method / Environmental Influences: temperature, osmotic pressure, and oxygen / Lab 6 Organisms Please take a few minutes to fill out a brief survey about your experience using the Virtual Edge: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1yGbkF0KM92WBSk-IgS-EkjxkTKTQwhzuXmDsVpwRDoU/viewform Please email comments/problems to cboggs@uwyo.edu |
|
Rachel Watson, M.S. |
|

The Virtual Edge by http://www.uwyo.edu/virtual_edge/ is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States License