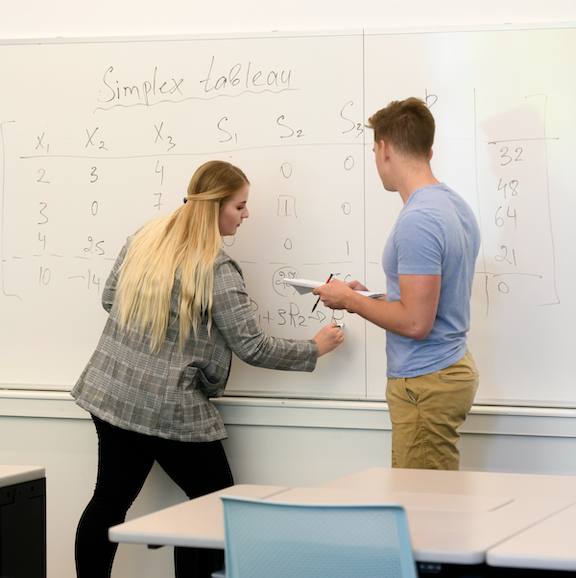Purposeful use of pauses within a lecture to emphasize important points and provide processing and questioning time.
Instructor poses a question and students write their answers on a piece of paper. They crumple it up and throw it at a box held by the instructor or learning assistant.

During a lecture pause or at the end of the lecture, the instructor or learning assistant asks the students to write down the concept that was most confusing. This can be done on paper or using a polling software.
Using technology or simpler way of displaying an answer to rapidly assess student understanding (& can then directly address misconceptions).
Students rate their perceived competence in completing a task or answering a question.
Engaging students in meaningful dialogue.
After working to solve a problem or answer a question, students post their responses (drawings or other creations) on the wall/around the room. Students then rotate around the room learning from fellow students/teams responses.
Students are each given a card or paper that contains a term, phrase or image that somehow connects to another student’s card or paper. Students are instructed to find their ‘match’ linking, terms and definitions, structure and function, item and image, for example.
Instructor or learning assistant poses an opinion question and ask people to stand in a particular location in the room based on their response.
Students are given or asked to take a stance on an issue. Student groups often work together for a few minutes to develop a statement, both sides share and rebuttals can continue as time allows.
Students evaluate a peer/s using clear guidelines describing expectations (e.g. a collaboratively generated rubric or charter).
Can have many forms but formally asks students to teach concepts that have already been presented by the instructor or outside resources. May involve students creating a video, skit, lecture, handout or presentation.
Have a subject matter expert available via text or another technology for real-time class discussion.
Students illustrate scientific components and processes.
Students use stories and narratives to make difficult scientific concepts more accessible and transferrable.
A real-life story or situation that encourages and allows students to explore/investigate issues related to a concept, often in effort to make a discovery or solve a case.
Students or student groups illustrate the relationships that exist between studied terms or concepts, often describing connections with short phrases or symbols on the constructed web or map.
Students are asked to create a representation of a system or process and design/develop/build a depiction.
Students use deep looking and reflect upon (and even handle) objects in order to expand the depth of their knowledge.
“A structured form of small group problem solving that incorporates the use of heterogeneous teams, maintains individual accountability, promotes positive interdependence, instills group processing, and sharpens social/leadership skills.” – Barbara Millis
Potentially taking many different forms, educators provide an active instructional session for students that often requires concept application to earn points or improve ranking compared to other students or student groups.

Simulations and Virtual Worlds
Potentially taking many different forms.

Enactments
Students act out specific parts or situations to enhance concept or process understanding.
Providing content material outside of class (i.e. through video) to allow for in-class activities.
Ensuring that each individual student meets the learning outcomes by designing instruction with students' interests, passions and goals in mind.
Student concept discovery and development through investigation (w/ leveled guidance).
A form of small-group learning that utilizes a flipped classroom, a readiness assurance process and application activitiesconcept discovery and development through investigation (w/ leveled guidance).
Students apply course concepts to describe and potentially solve a selected problem.
Knowledge, skill and value development from direct experience, reflection, conceptualization and experimentation often outside a traditional academic setting (i.e. internships, study abroad, undergraduate research, residency programs, etc.).
Applying course content to assist and provide a service for an organization, group or individual in the community.
Learning that embeds in the local environment and values students’ experience.
Employs a diverse group of learners in solving real-world, complex and urgent problems.
Sharing with Students!
While enacting active learning modalities through best practices is one very important piece of nurturing student learning, when educators share their philosophies and reasons for adopting evidence-based practices, students' learning can be enhanced even more. In the vodcast below, Dr. Tawfik Elshehabi of UW's Petroleum Engineering Department facilitates a LAMP Coffee & Curriculum Session entitled When We Care, We Share: Empowering Students with an Innovative Visual Teaching Philosophy.